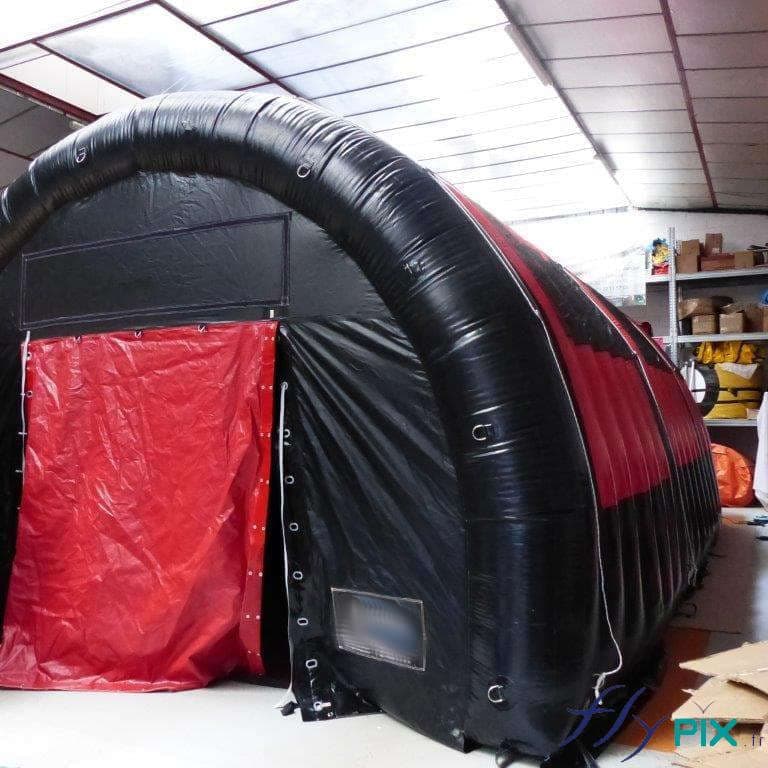
Storage mobile inflatable tents stations, for the storage and maintenance of medical equipments
Some examples of custom-made inflatable mobiles shelters or sheds for the storage of medical and first aid supplies and resources.
Inflatable military shelters have become essential assets for modern armed forces, offering rapid deployment, superior adaptability, and resilience in diverse operational environments.
Constructed from high-durability PVC envelopes and available in captive air or ventilated configurations, these structures serve critical roles in storage, equipment protection, maintenance, and vehicle repair.
In contemporary military operations, the ability to rapidly establish secure and efficient facilities for storage and maintenance is paramount.
Inflatable military shelters provide an innovative solution, combining portability, durability, and cost-effectiveness.
These structures, typically made from reinforced PVC membranes, are designed for air retention (captive air) or continuous ventilation, ensuring stability in extreme weather conditions and high-demand operational settings.
Their applications extend from safeguarding mission-critical equipment to housing vehicle repair stations in forward operating bases.
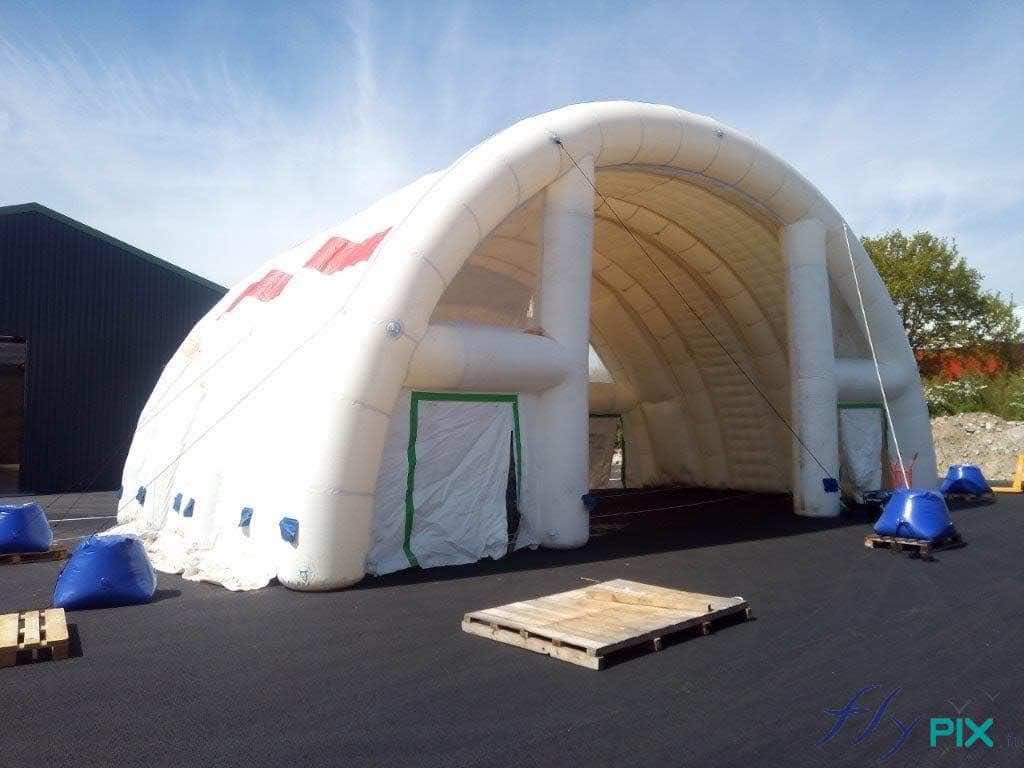

Why use mobile inflatable shelters, tents, and inflatable hangars to store medical or military equipment, supplies, and equipment? Medical Storage:
- Protecting vital resources (medicines, food, water, supplies)
- Medical Equipment Shelter: Advanced diagnostics and treatments, inventory of medical equipment and supplies
- Military Storage: Securing the tools of war
- Weapons and Ammunition Safes: Reinforcing lethal arsenals, centralizing and facilitating access to weapons resources in conflict or war situations
- Vehicle Shelter: Protecting mobile military power from the elements, wind, rain, and snow
- Maintenance and Repair of Tanks or Other Military Vehicles in Wartime: Ensuring the resilience and availability of armored vehicles in the field
- Aircraft Maintenance: Ensuring the sustainability of aerial surveillance platforms, maintaining and repairing aircraft and combat helicopters
- Aircraft Repair Shops: Keeping wings flying in conflict zones, repairing aircraft or helicopter engines
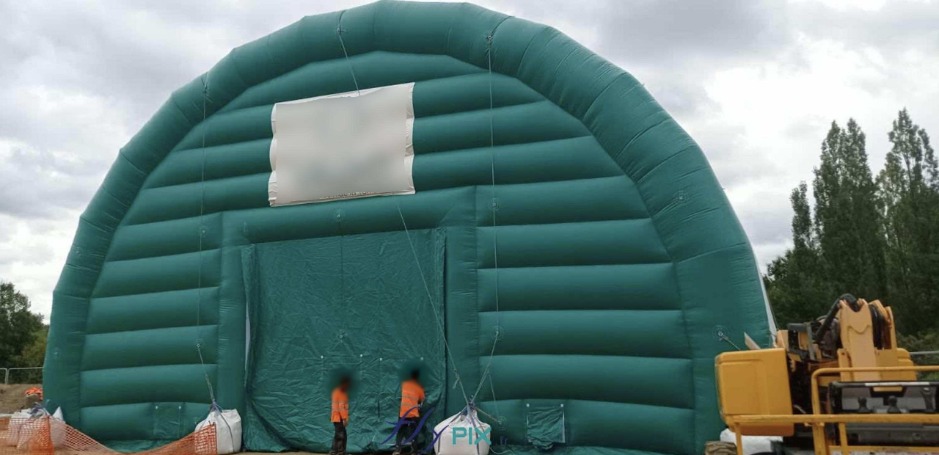

In the unforgiving theaters of war and the chaotic aftermath of disaster, mobile inflatable shelters, tents, and hangars have emerged as unsung heroes.
These versatile, air-supported structures transcend traditional logistics, offering robust solutions for storing medical equipment, housing sophisticated machinery, safeguarding military hardware, and maintaining heavy assets like tanks, aerostats, and aircraft.
Lightweight yet resilient, they provide commanders and medics alike with a tactical edge—rapid deployment, adaptability, and protection against the elements and enemy action.
Storage Benefits
- Rapid Deployment: Erected in minutes, ensuring immediate asset availability.
- Portability: Lightweight, collapsible for air, land, or sea transport.
- Environmental Protection: Weatherproof, UV-resistant, and antifungal materials.
- Security: Lockable, camouflaged, and reinforced against theft or sabotage.
- Scalability: Modular designs for small caches or theater-wide stockpiles.
Medical Applications
- Equipment Safety: Preserves sterility and functionality of medical tools.
- Machinery Housing: Shields advanced diagnostics (e.g., MRI, ventilators) from damage.
- Climate Control: Maintains optimal conditions for sensitive devices.
- Triage Support: Facilitates rapid setup of treatment zones.
- Contagion Prevention: Integrates PPE storage and biohazard safeguards.
Military Utility
- Gear Protection: Secures comms, optics, and recon equipment.
- Weapons Security: Fortifies arms and ammo against enemy action.
- Vehicle Sheltering: Shields fleets from weather and wear.
- Tactical Flexibility: Adapts to shifting operational needs (e.g., FOBs, C2 nodes).
- Concealment: Camouflage and low-profile options evade detection.
Maintenance and Repair
- Tank Support: Enables field repairs of tracks, engines, and armor.
- Aerostat Maintenance: Sustains surveillance balloons with minimal downtime.
- Aircraft Upkeep: Houses repair bays for jets and choppers in theater.
- Tool Integration: Stores and organizes repair kits and heavy machinery.
- Resilience: Dust-free, stable environments for precision work.
Strategic Advantages
- Force Multiplier: Enhances operational tempo and readiness.
- Logistical Agility: Reduces supply chain burdens in austere zones.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Lower expense than permanent structures.
- Future-Proofing: Adapts to emerging tech (e.g., smart materials, drones).
- Global Reach: Deployable in any conflict or crisis scenario.
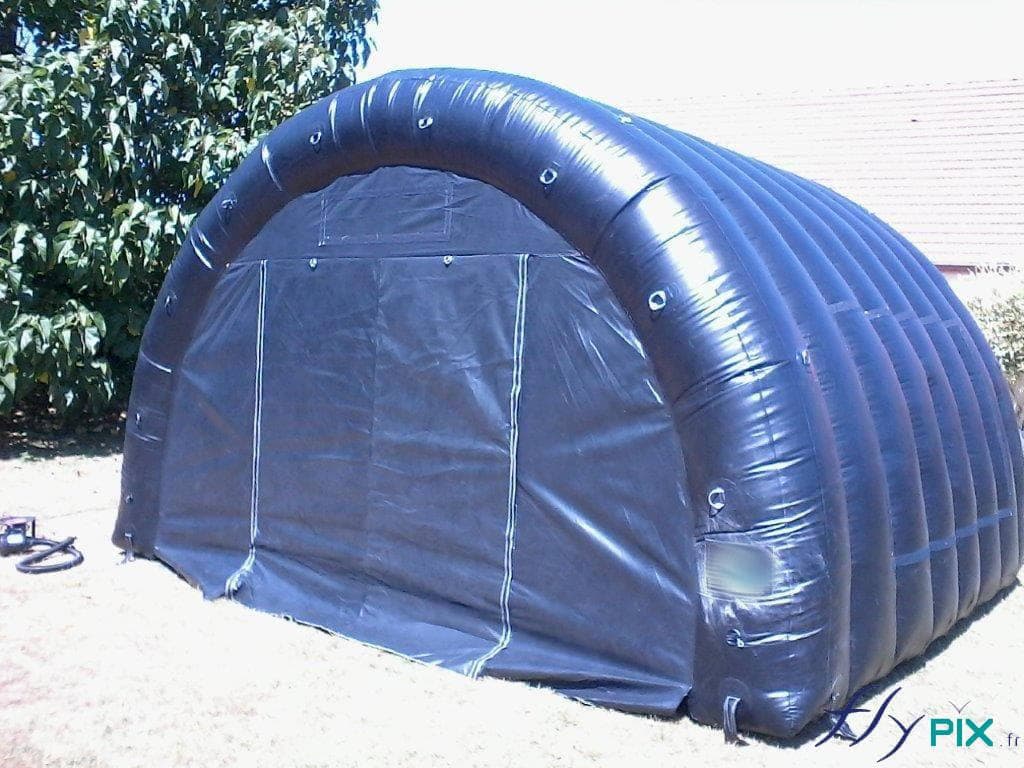
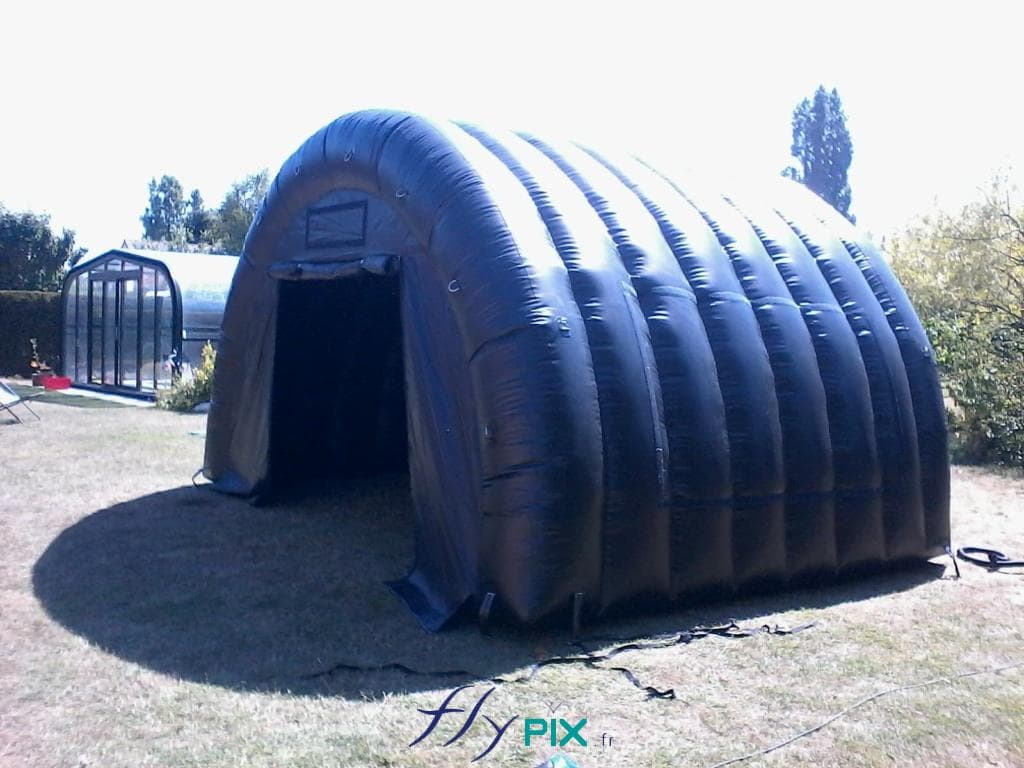
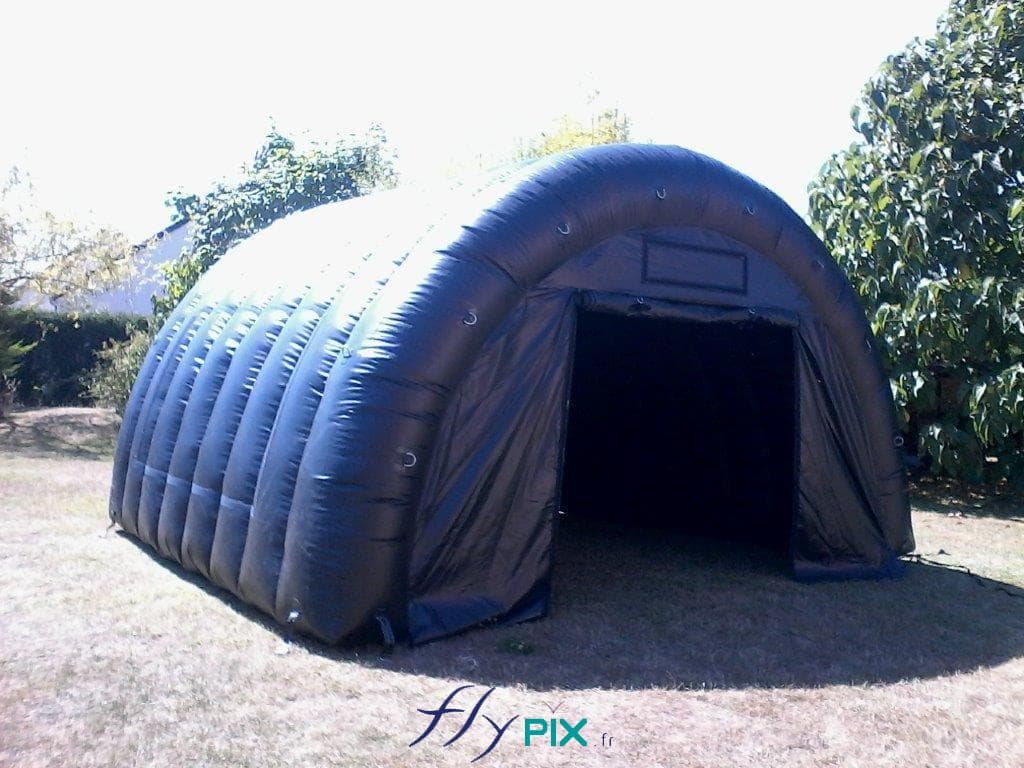
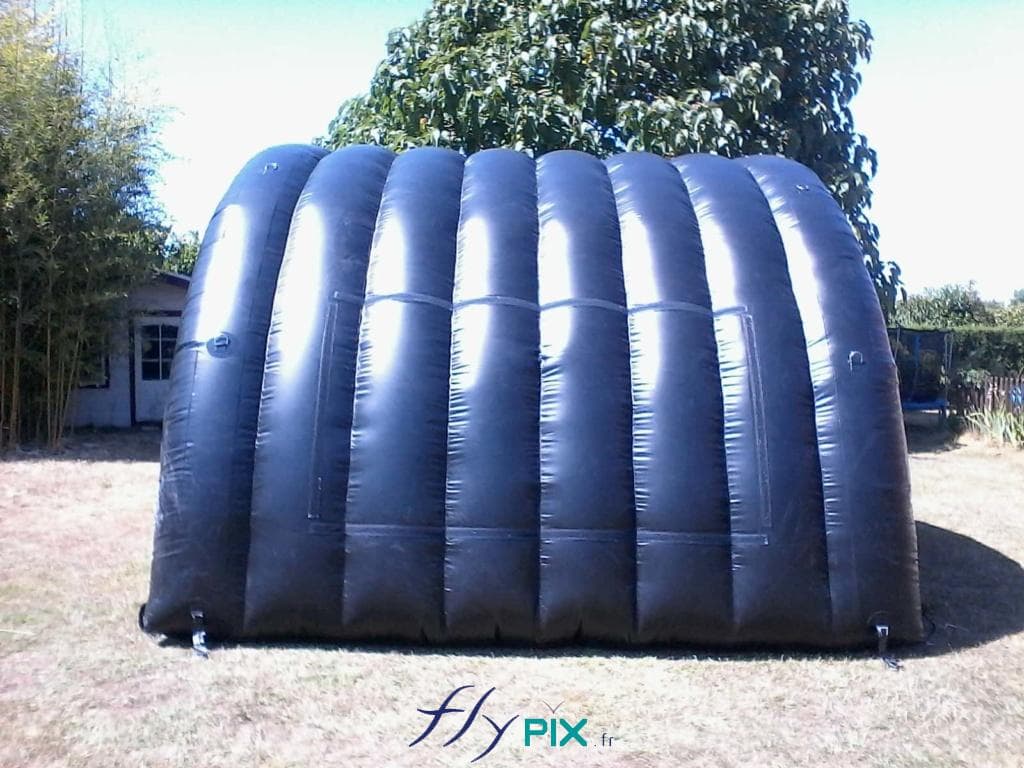





Military-grade inflatable shelters are constructed using high-density PVC-coated fabrics, which offer resistance against UV radiation, extreme temperatures, and mechanical wear.
These structures incorporate reinforced seams and multilayer coatings to enhance tensile strength, ensuring longevity and operational reliability.
The dawn of inflatable shelters has ushered in a paradigm shift, melding agility with durability in the crucible of conflict and calamity.
These air-inflated edifices—ranging from modest tents to sprawling hangars—stand as testaments to human ingenuity, addressing the perennial challenges of storage, maintenance, and operational sustainment in austere environments.
No longer relegated to rudimentary encampments, they now cradle the sinews of modern warfare: medical apparatus that mends the wounded, military machinery that dictates battlefield supremacy, and armored behemoths that project power.
Their ascent is not accidental but a response to the exigencies of asymmetric warfare, global pandemics, and resource scarcity.
Historically, military and medical logistics leaned on ponderous, static infrastructure—warehouses of concrete and steel, vulnerable to bombardment, or canvas tents prone to collapse under duress.
Inflatable shelters, by contrast, harness airbeam technology, high-tensile fabrics like polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU), and modular designs to erect fortified sanctuaries in mere hours.
A forward operating base (FOB) can spring to life amidst a desert storm, a field hospital can rise on a flood-ravaged plain, and a repair bay can shelter a crippled aircraft—all with a fraction of the manpower and time demanded by traditional methods.
This introductory salvo charts the lineage of these structures, from their nascent use in humanitarian aid to their current prominence in joint task force operations and theater-level engagements.
It frames their utility across the spectrum of needs—storing delicate endoscopes alongside rugged howitzers, servicing tanks amidst artillery barrages, and shielding aerostats from sand-laden gales.
Terms like “expeditionary logistics,” “force projection,” and “critical care continuum” pepper the discourse, setting the stage for a granular exploration of their advantages in the sections to follow.
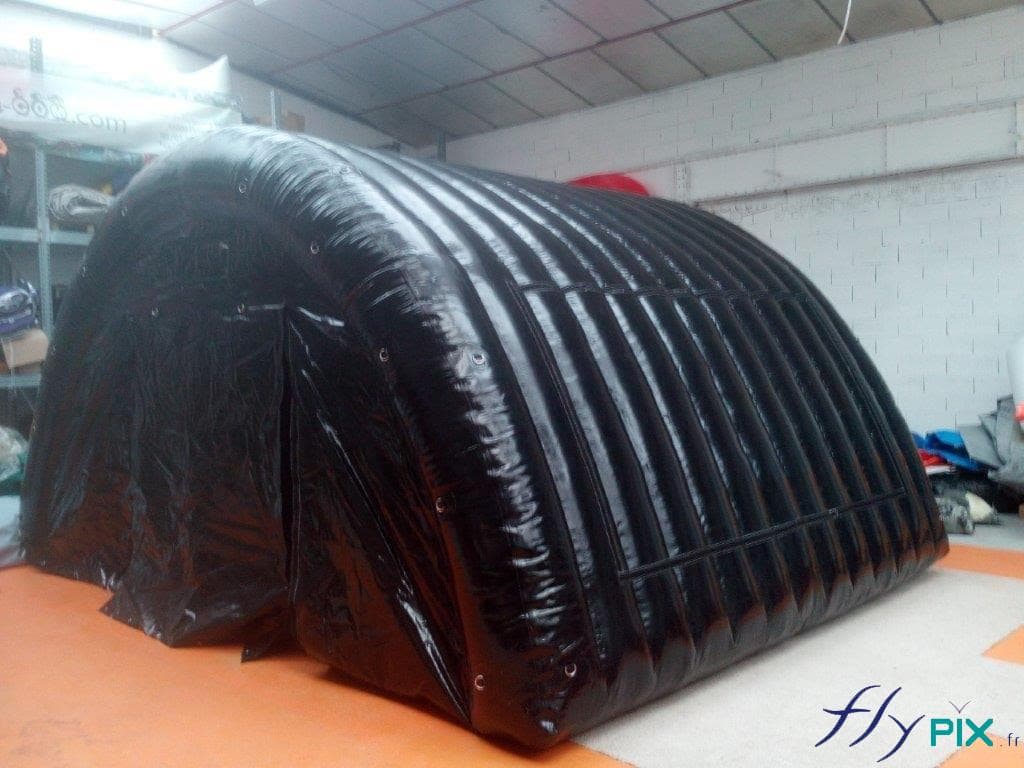


Inflatable shelters are designed to withstand high winds, heavy snowfall, and rapid temperature fluctuations.
Military-grade shelters are rigorously tested for durability, ensuring they are resistant to harsh environments.
Inflatable shelters can be deployed in a matter of minutes to hours, depending on size.
Their modular design allows for interconnectivity, facilitating scalable solutions for varying operational demands.
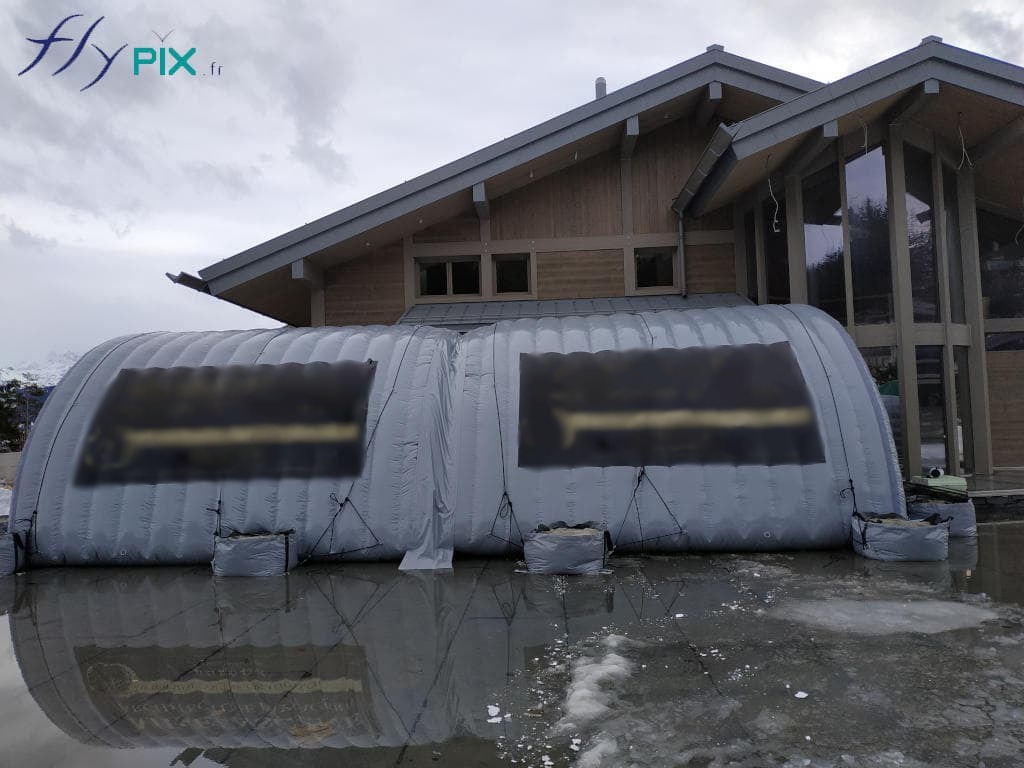
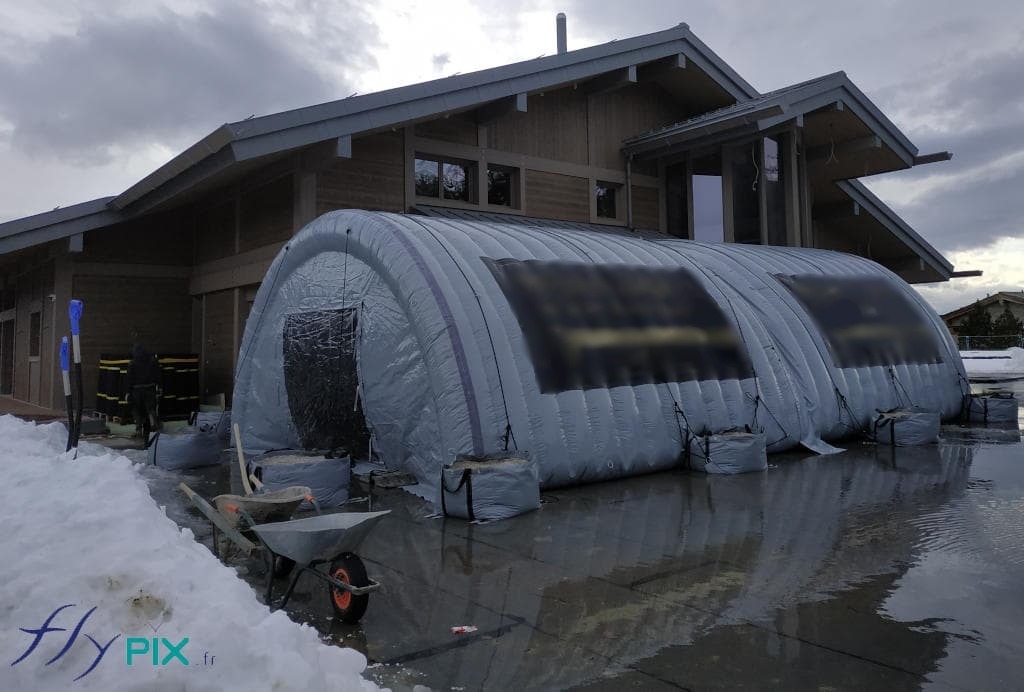
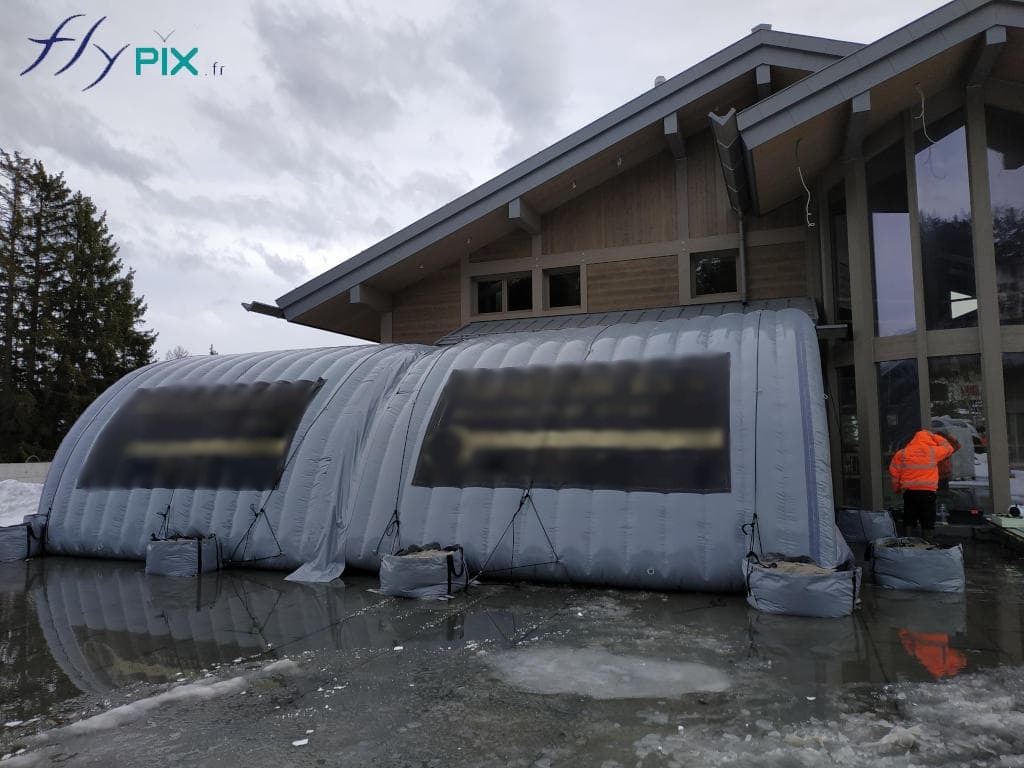
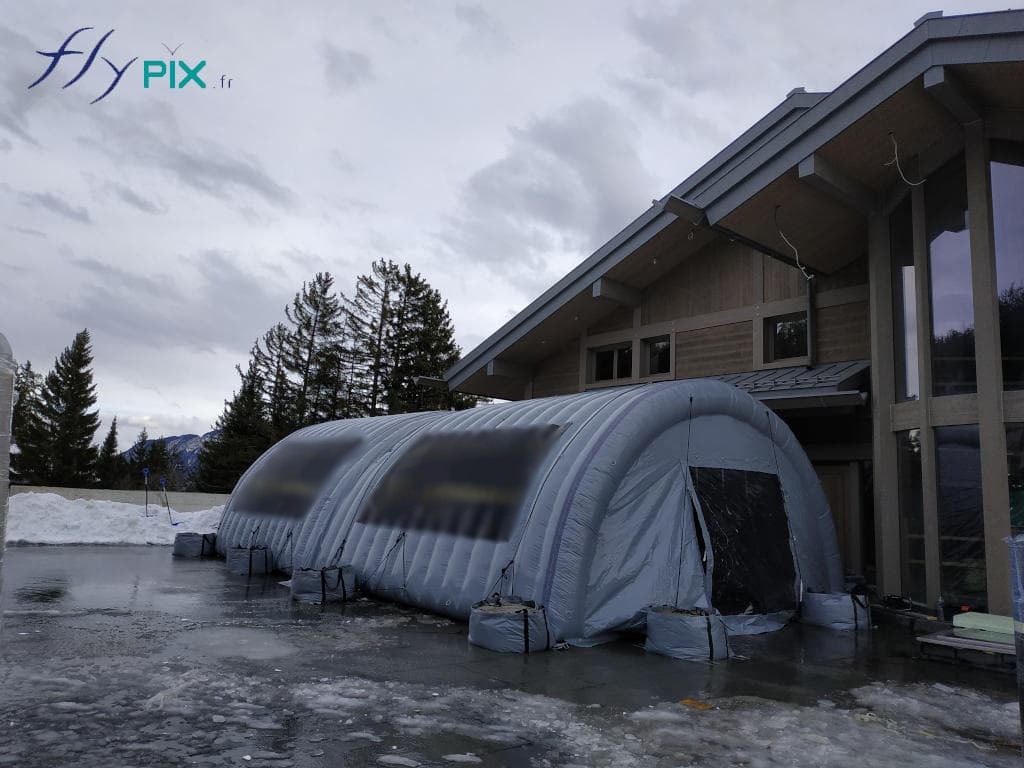
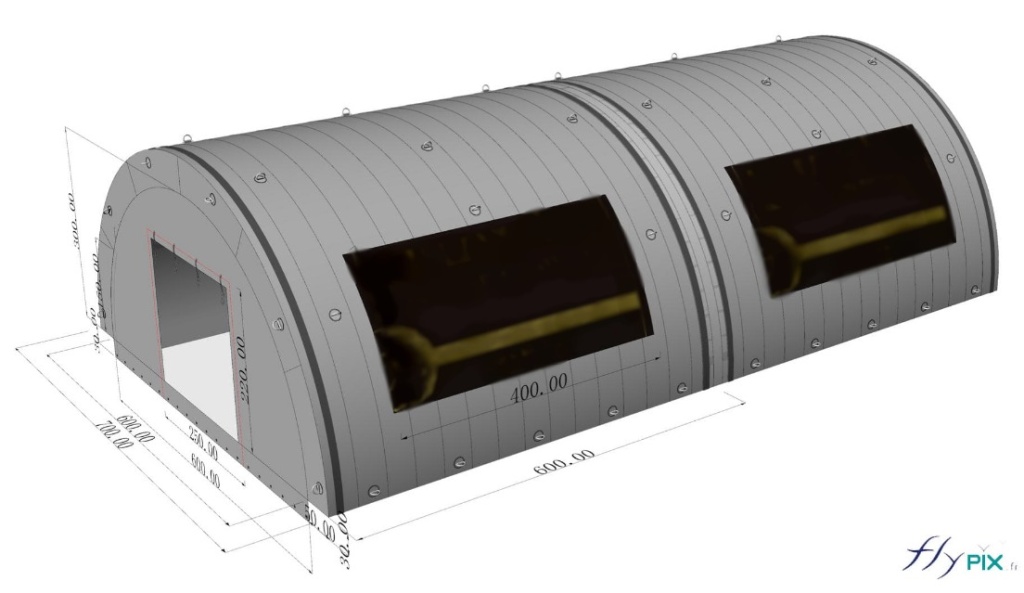




These shelters maintain operational integrity in deserts, Arctic zones, and humid jungles. Advanced ventilation systems regulate internal.
In the relentless arena of conflict and crisis, the sanctity of medical equipment is non-negotiable.
Mobile inflatable shelters, tents, and hangars rise as stalwart guardians, offering a haven for the tools that suture wounds, resuscitate the fallen, and stave off the specter of infection.
These portable bastions—erected with alacrity and fortified against the caprices of nature—ensure that bandages, defibrillators, ventilators, and surgical kits remain pristine, accessible, and primed for deployment, whether on a battlefield littered with shrapnel or a refugee camp teeming with the displaced.
The paramount advantage of inflatable shelters lies in their rapid emplacement, a virtue that military logisticians dub “time-to-task capability.”
A standard medical supply cache—encompassing sterile gauze, intravenous (IV) fluids, tourniquets, and portable ultrasound units—can be ensconced within an inflatable tent in under 30 minutes.
Contrast this with the days required to erect a rigid storage depot, and the tactical dividend becomes clear: medics gain immediate access to their arsenal, enabling them to execute the “golden hour” protocol—stabilizing casualties before irreversible damage sets in.
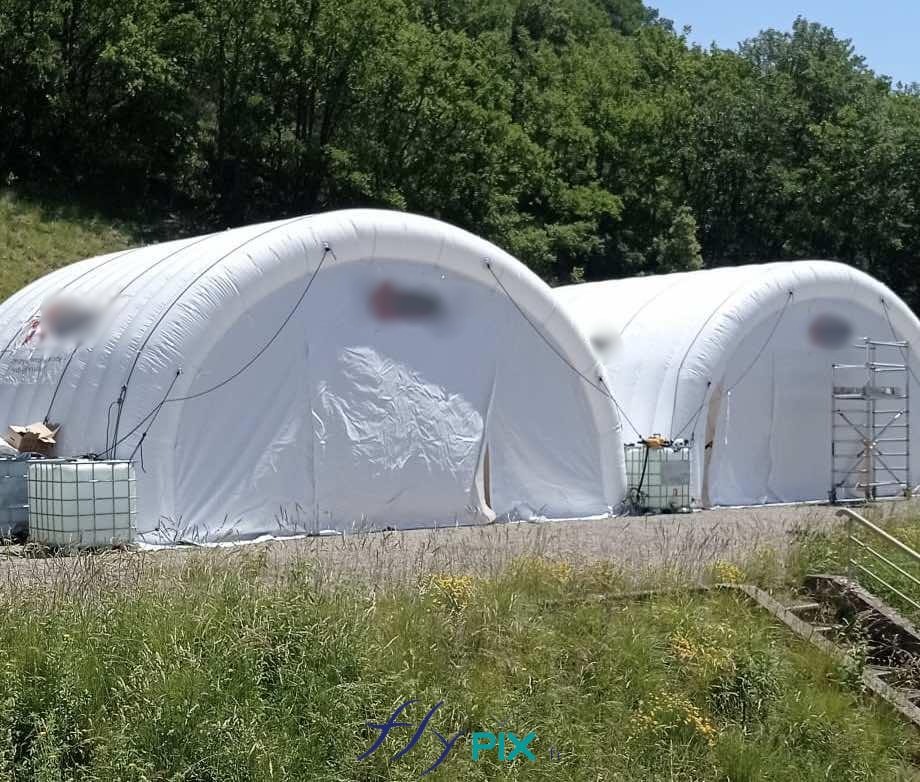

The jargon of emergency medical services (EMS)—“point-of-injury care,” “mass casualty incident (MCI),” “patient evacuation (MEDEVAC)”—underscores this urgency, where every minute shaved off logistics amplifies survival odds.
Beyond speed, these shelters boast environmental resilience, a bulwark against the elements that threaten medical materiel.
Constructed from weatherproof fabrics—often impregnated with UV-resistant coatings and antifungal agents—they repel rain, dust, and extreme temperatures that could degrade latex gloves, corrode metal instruments, or spoil pharmaceuticals like antibiotics and analgesics. In a desert theater, where sandstorms scour unprotected gear, or a tropical zone where humidity fosters mold, an inflatable storage unit maintains a controlled microclimate.
Integrated ventilation systems, sometimes augmented with HEPA filters, ensure air purity, safeguarding against airborne contaminants that could compromise sterile fields or respiratory equipment.
Portability is another linchpin of their utility. Weighing a fraction of traditional storage modules, inflatable shelters collapse into compact, transportable packages—ideal for airlift by C-130 Hercules, ground haul via Humvee, or even manual carry by a small squad.
This mobility is a godsend in fluid operational zones, where a brigade combat team (BCT) might relocate its medical supply point (MSP) overnight to support a flanking maneuver, or a humanitarian NGO might shift its stockpile to a newly accessible village.
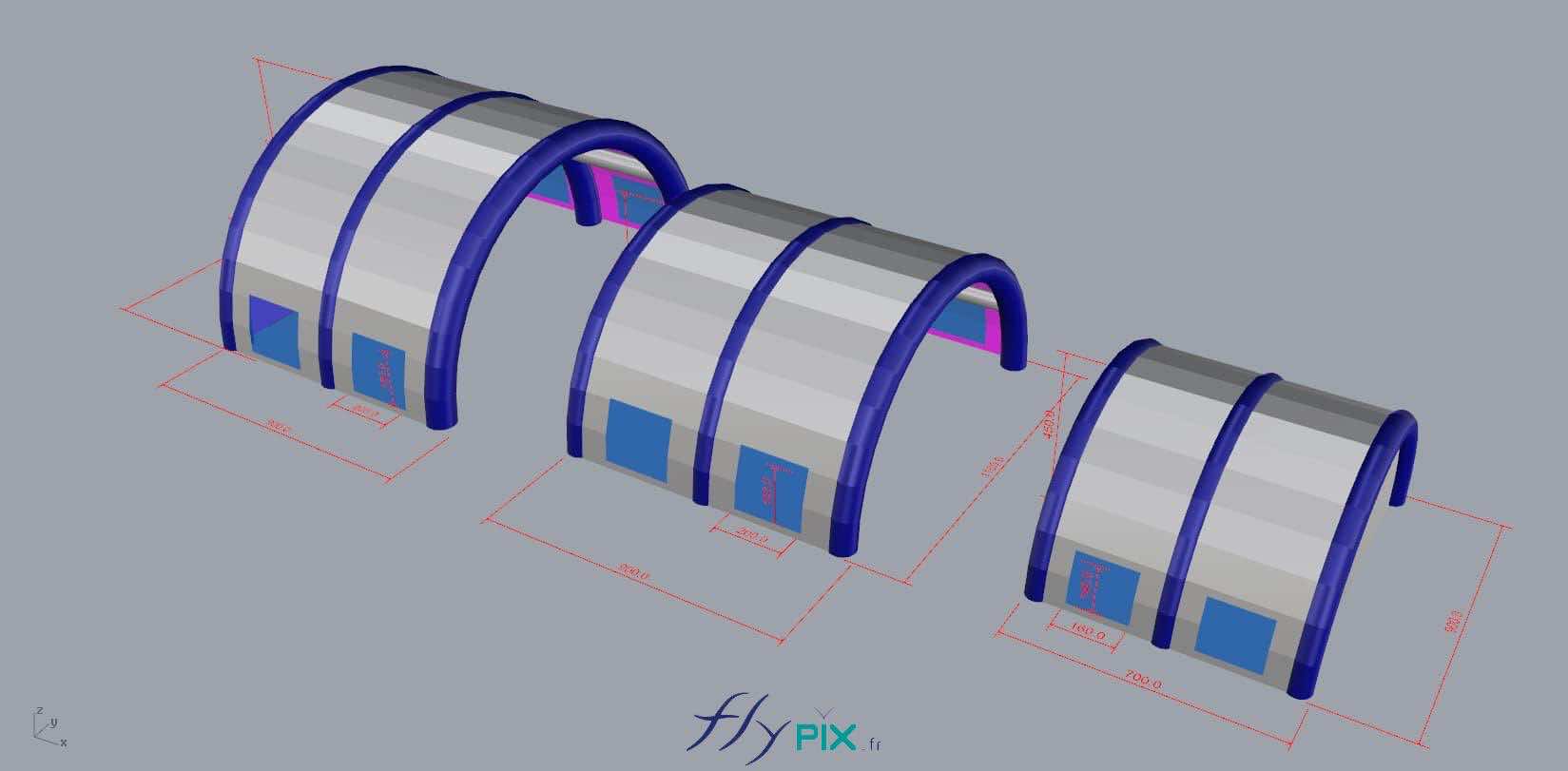
The military lexicon—“expeditionary footprint,” “logistical agility,” “sustained ops”—captures this flexibility, allowing commanders to project medical readiness wherever the fight or the need arises.
Security, too, is paramount. Inflatable shelters can be reinforced with ballistic-grade linings or camouflaged to evade enemy reconnaissance—be it human intelligence (HUMINT) or unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) surveillance.
Lockable airlocks and tamper-proof seams deter pilferage, ensuring that morphine ampoules, blood transfusion kits, and diagnostic reagents remain in allied hands.
In conflict zones rife with insurgents or looters, this fortification transforms a mere tent into a stronghold, preserving the materiel that underpins the “combat lifesaver” (CLS) mission—staunching hemorrhages, restoring airways, and treating shock.

Scalability rounds out their advantages. A single inflatable unit might house a basic first aid kit for a platoon, while a linked network of hangars can store an entire theater-level medical supply chain—think portable X-ray machines, autoclaves, and crates of personal protective equipment (PPE).
This modularity adapts to the mission’s scope, whether supporting a special forces raid or a multinational disaster response.
Case studies abound: during Operation Inherent Resolve, inflatable shelters stockpiled trauma gear for coalition medics, while in Ebola-ravaged West Africa, they warehoused hazmat suits and antiviral drugs, thwarting contagion.
In sum, inflatable shelters for medical equipment storage are not mere conveniences—they are strategic imperatives.
They meld speed, resilience, mobility, security, and adaptability into a cohesive solution, ensuring that the instruments of healing remain at the ready, unbowed by the chaos of war or the ravages of nature.
As the backbone of field medicine, they empower caregivers to defy the odds, one life at a time.
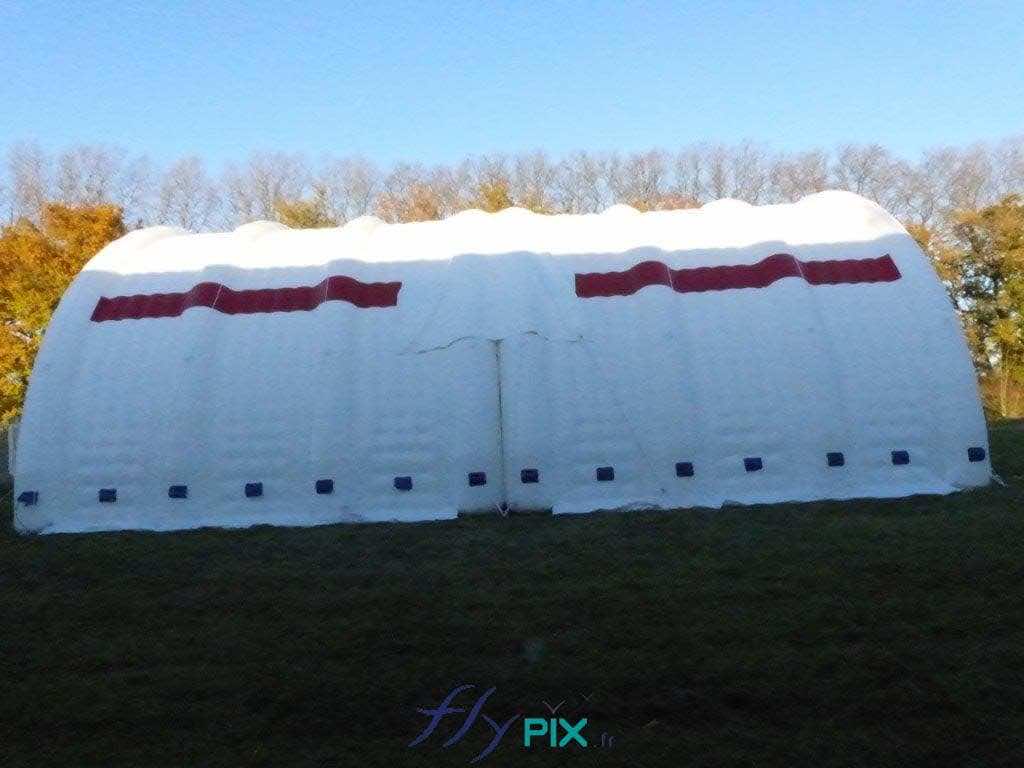
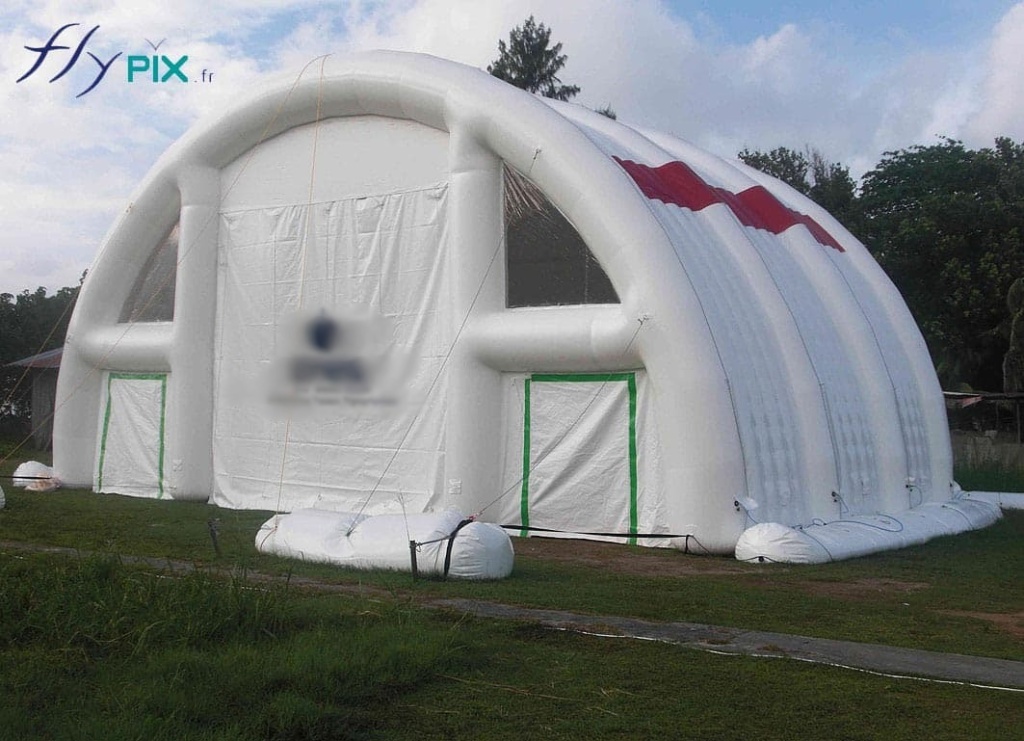
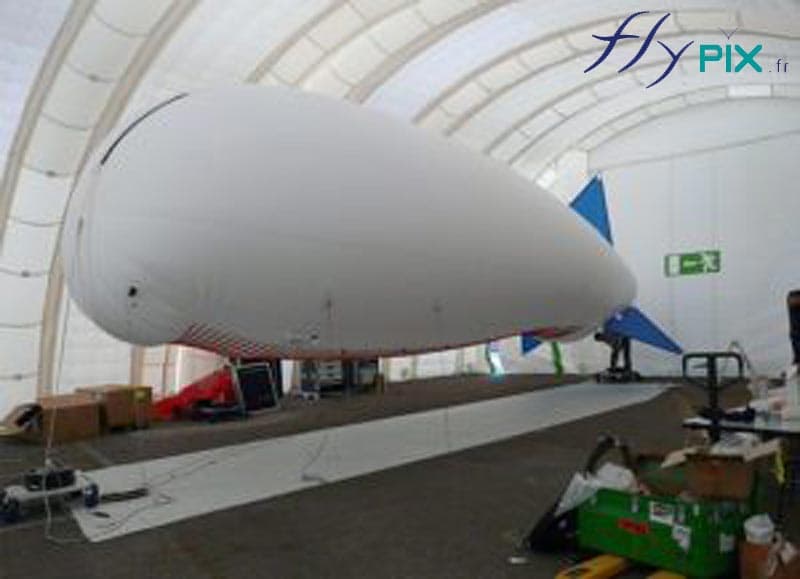
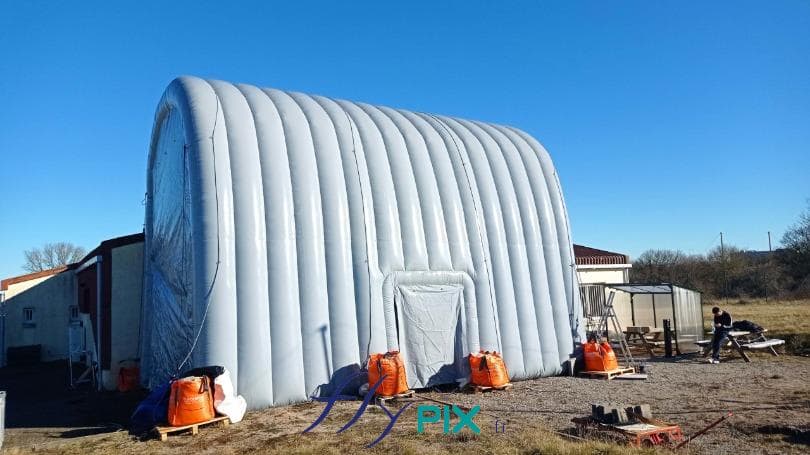
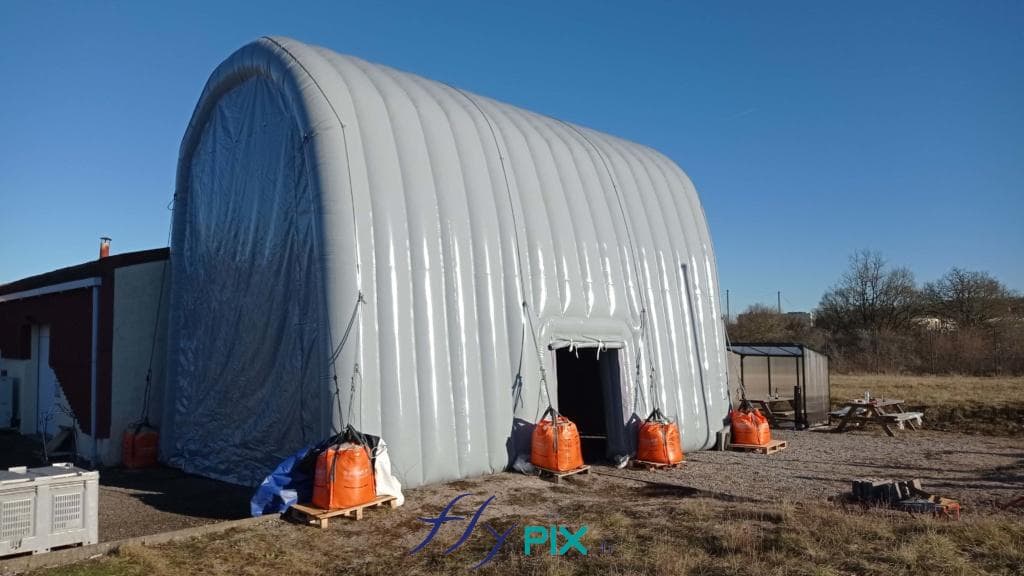
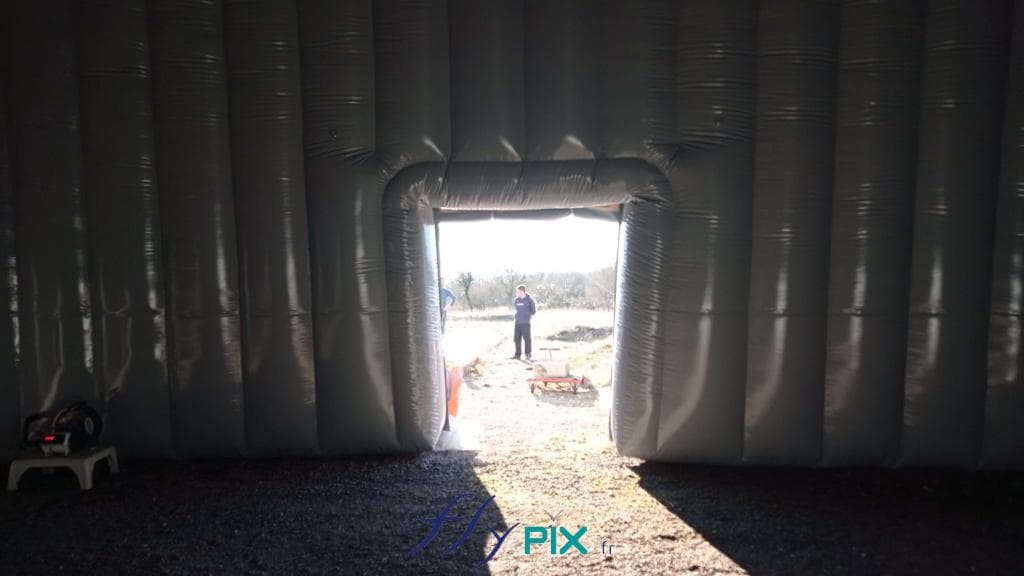
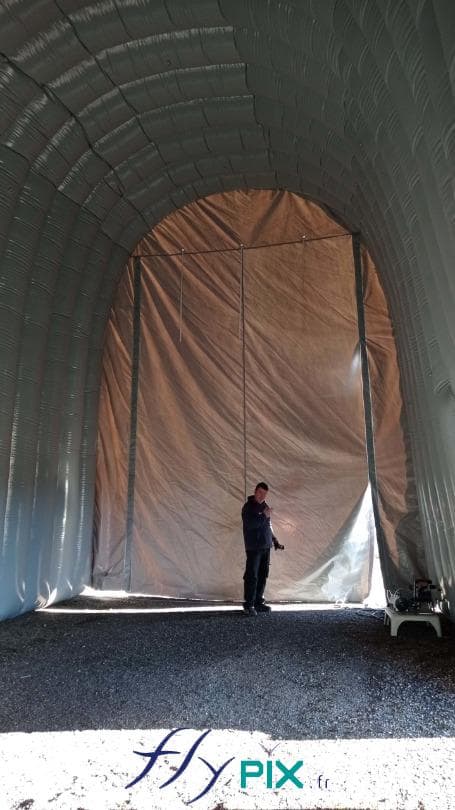
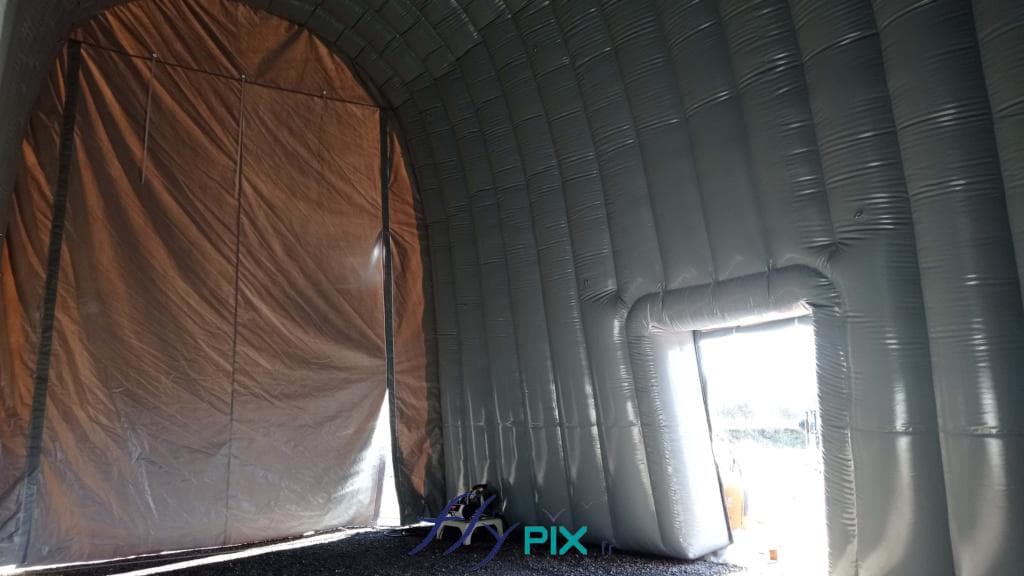
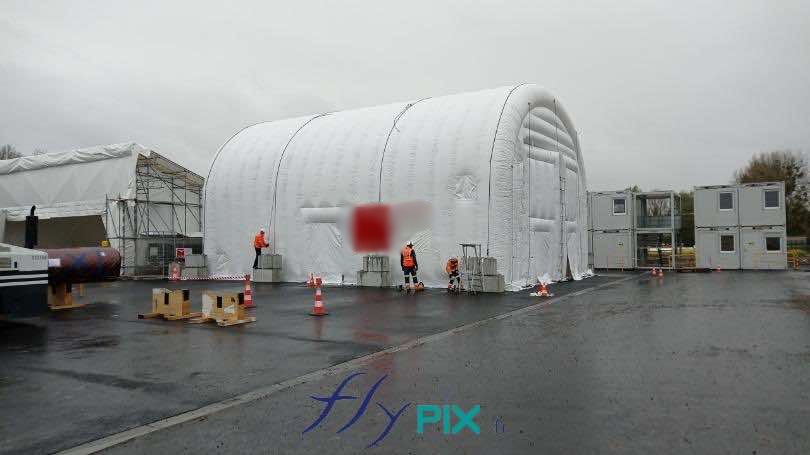
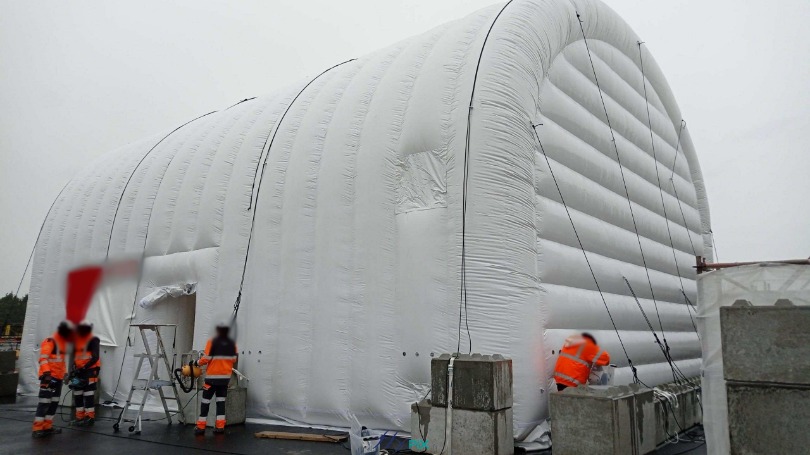
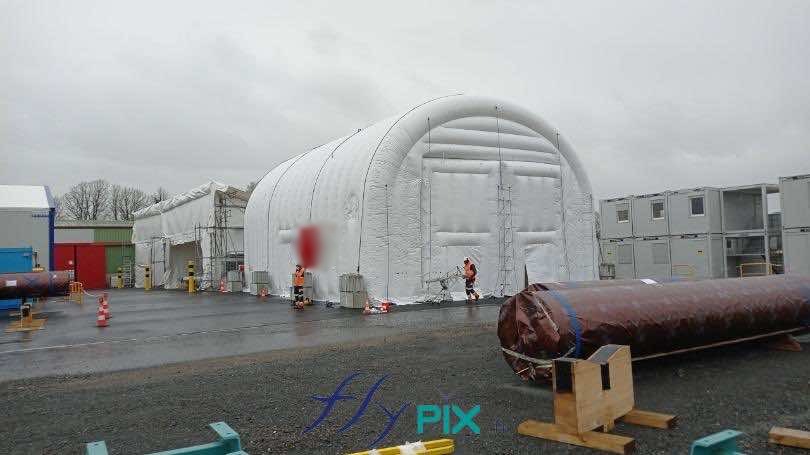
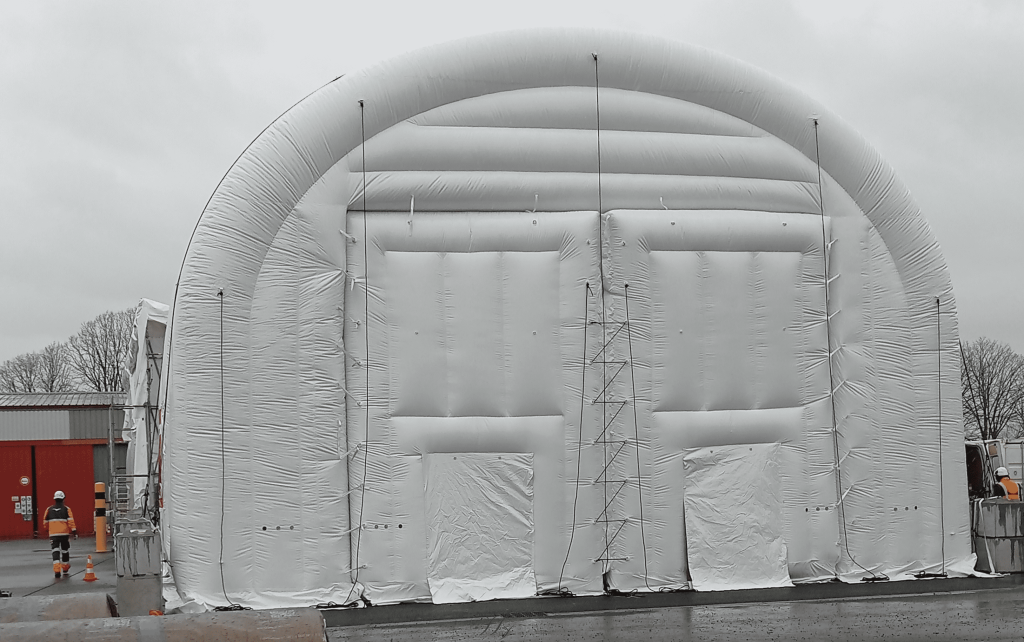
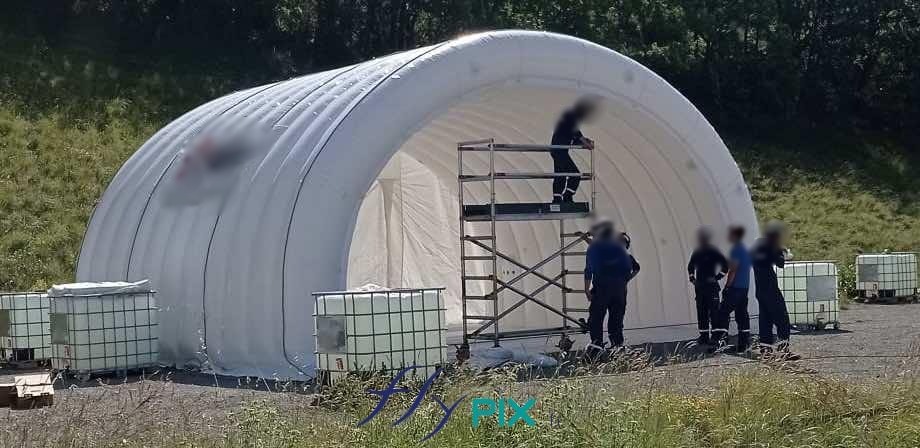



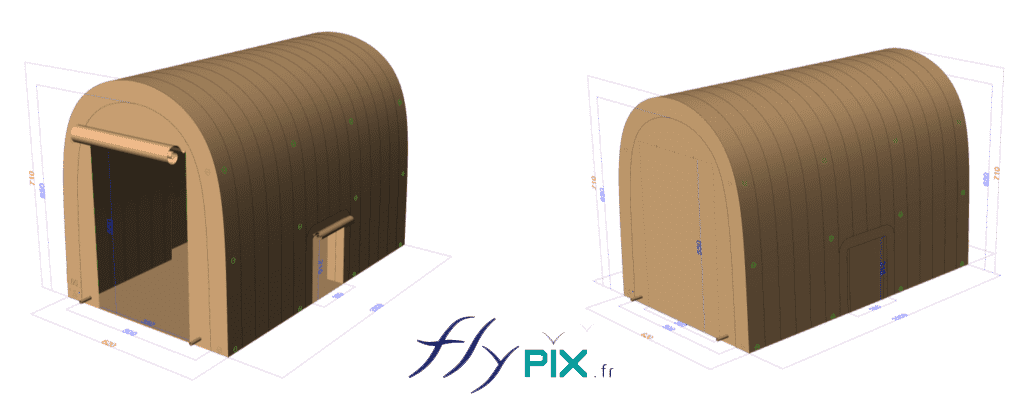






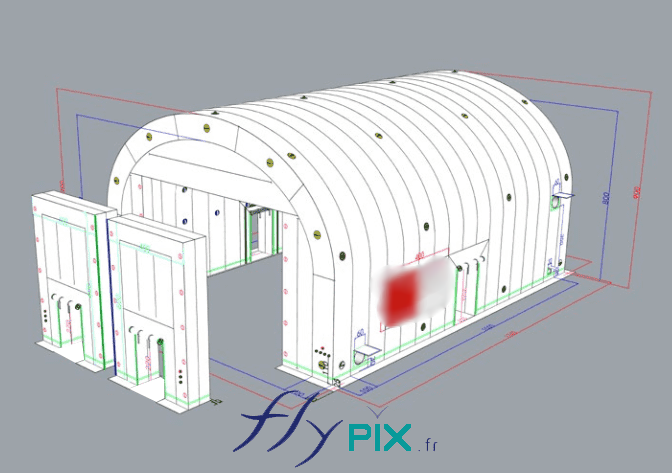





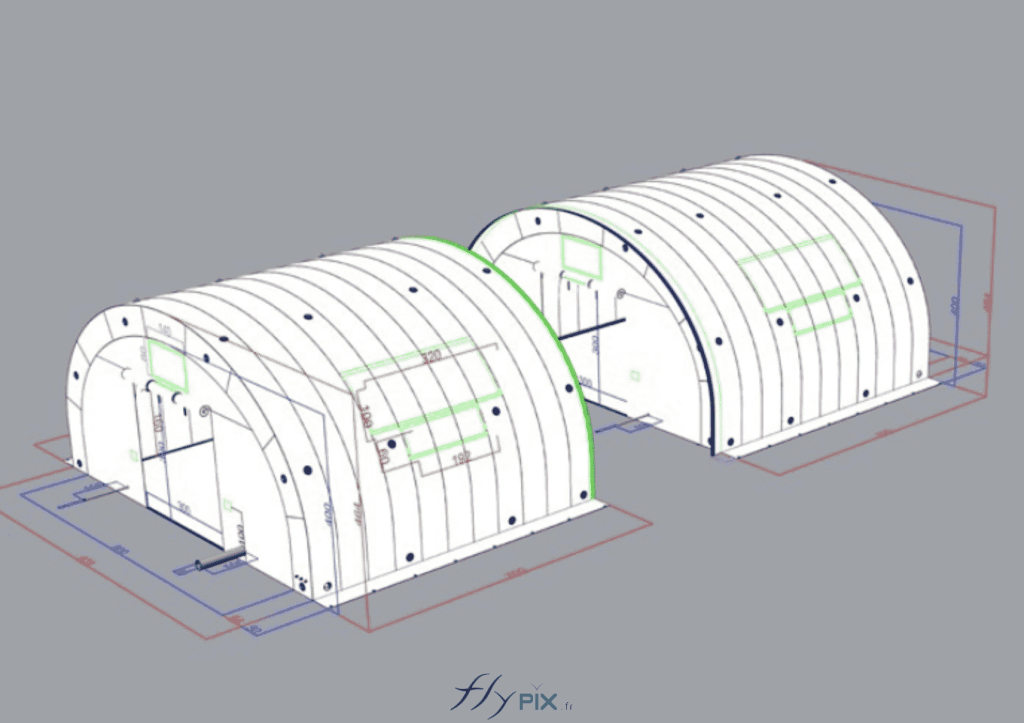
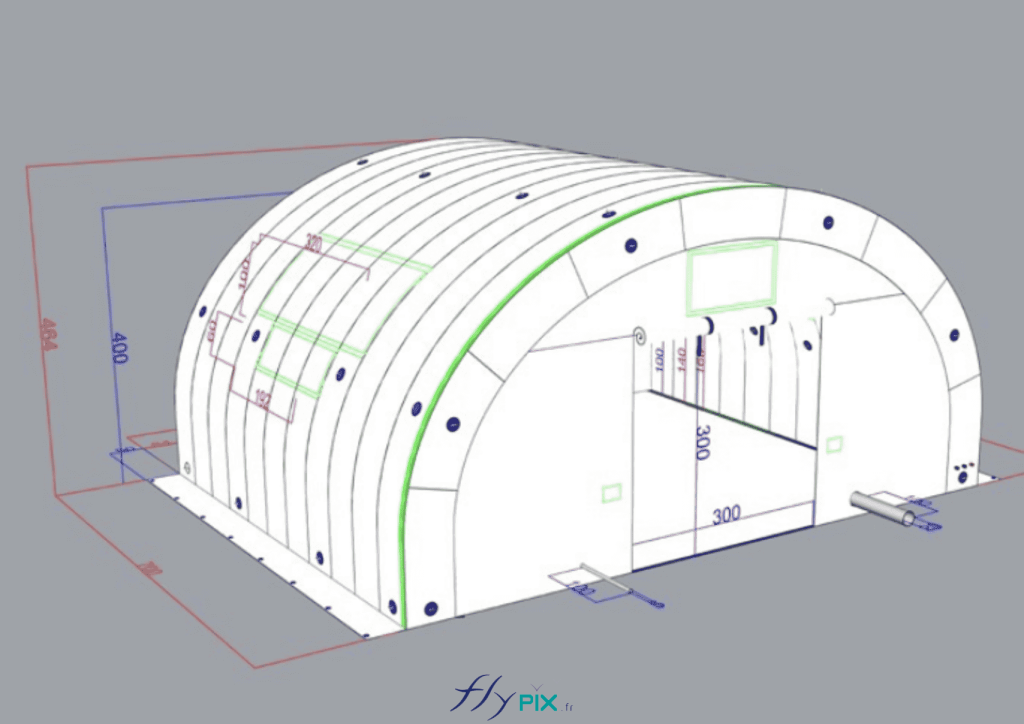
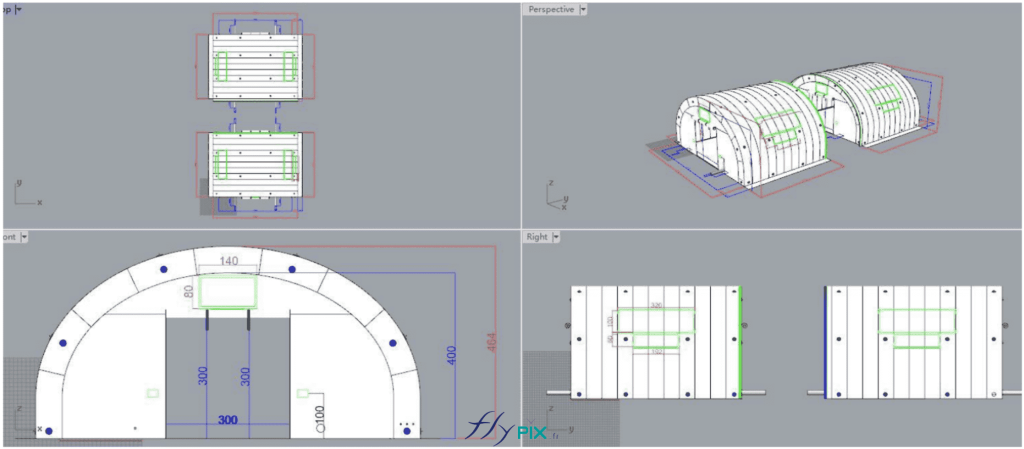



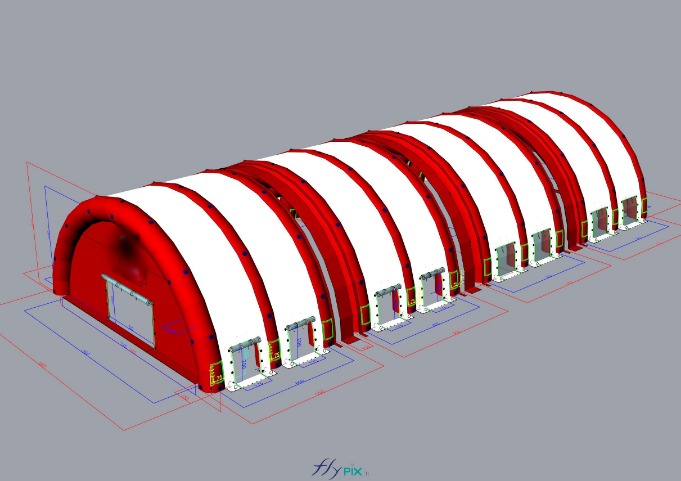
Inflatable military shelters, tents, and hangars provide indispensable advantages in modern warfare and operational logistics.
Their ability to rapidly deploy, protect critical assets, and enhance operational efficiency makes them a cornerstone of military infrastructure.
Future innovations will continue to improve their resilience, adaptability, and sustainability, ensuring their continued relevance on the battlefield and beyond.
